As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, old smartphones often find themselves discarded or replaced. However, the journey of these devices does not end when they are dropped off for recycling. Understanding what happens to old smartphones after recycling is crucial for consumers who wish to minimize their environmental impact and contribute to a more sustainable future.
The Recycling Process Explained
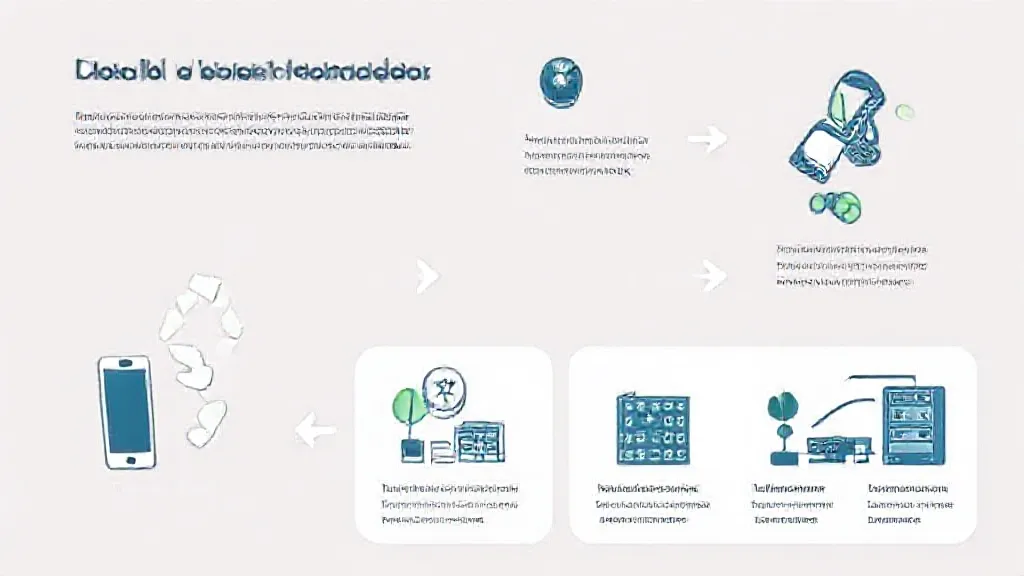
When smartphones are recycled, they typically go through a multi-step process that begins with collection and sorting. Recycling centers gather devices from various sources, including retail drop-off programs, collection drives, and e-waste events. Once collected, the smartphones are sorted by type and brand, and any reusable accessories, such as chargers and cases, are separated for resale or donation.
Dismantling and Component Recovery
The next step in the recycling process involves dismantling the smartphones. Skilled workers or automated machines carefully disassemble the devices to recover valuable components. This includes extracting metals like gold, silver, copper, and aluminum, which are essential for manufacturing new electronics.
Additionally, plastics and glass are separated for recycling. The recovery of these materials is vital, as it reduces the need for mining and lowers the environmental impact associated with resource extraction.
Hazardous Materials Management
Old smartphones also contain hazardous materials, such as lithium-ion batteries, lead, and cadmium.
Proper recycling processes ensure that these substances do not harm the environment. Recycling facilities are equipped to handle hazardous materials safely, following strict regulations to prevent contamination of soil and water. This aspect of recycling is crucial as improper disposal can lead to severe environmental consequences.
Refurbishment vs. Recycling
Not all old smartphones are sent directly to recycling. Many devices are refurbished, meaning they are repaired and restored to a functional state before being resold.
This process extends the life of the device and reduces the demand for new products. Refurbished smartphones often come with warranties and can be a cost-effective alternative for consumers. The refurbishment process contributes significantly to waste reduction and promotes a circular economy.
Environmental Impact and Benefits
Recycling old smartphones has significant environmental benefits. By recovering valuable materials, recycling reduces the need for new raw materials, which in turn decreases energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions associated with mining and manufacturing. Furthermore, recycling helps to mitigate the growing problem of electronic waste (e-waste), which is one of the fastest-growing waste streams globally.
Consumer Awareness and Responsibility
As consumers, it is essential to understand the recycling options available for old smartphones. Many manufacturers and retailers offer take-back programs, allowing users to return their devices for proper recycling or refurbishment. Educating oneself about local recycling facilities and e-waste regulations can empower consumers to make informed decisions regarding their electronic devices.
Future Innovations in Smartphone Recycling
The future of smartphone recycling looks promising, with ongoing innovations aimed at improving efficiency and sustainability. Researchers are developing new methods for extracting materials from electronic waste, such as bioleaching, which uses microorganisms to recover metals. Additionally, companies are exploring modular designs for smartphones, enabling easier repairs and upgrades, thus reducing waste.
Conclusion: The Importance of Recycling Old Smartphones
In conclusion, the journey of old smartphones after recycling is a complex process that involves careful dismantling, material recovery, and hazardous waste management. By understanding this lifecycle, consumers can appreciate the importance of recycling and the positive impact it has on the environment. As technology continues to advance, responsible recycling practices will play a critical role in creating a sustainable future for electronic devices.