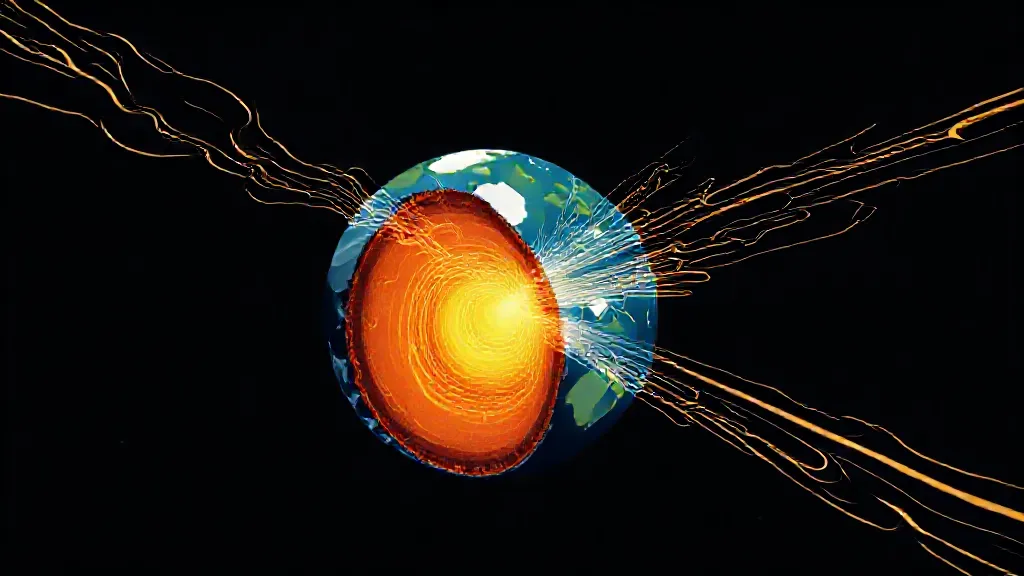
The Earth’s magnetic field is an essential aspect of our planet, influencing everything from navigation to the protection of life against solar radiation. But where does this magnetic field come from? The answer lies in the complex interplay of the Earth's inner structure, particularly its core, and the dynamics of fluid motion within it.
The Core: The Heart of Earth's Magnetism
At the center of the Earth is the core, which is primarily composed of iron and nickel.
This core is divided into two parts: the solid inner core and the liquid outer core. The outer core is where the magic happens. The movement of molten iron in this layer generates electric currents.
According to the dynamo theory, these electric currents produce magnetic fields, which combine to create a strong and coherent magnetic field that extends far beyond the surface of the Earth.
The Dynamo Effect Explained
The dynamo effect is crucial to understanding how the Earth's magnetic field is generated. As the Earth rotates, the fluid motion of the outer core is influenced by this rotation, creating complex patterns of convection.
Hot iron rises while cooler, denser iron sinks, generating a continuous flow of conductive material. This movement of electrically conductive fluids in the presence of the Earth’s rotation generates a self-sustaining magnetic field.
Historical Perspectives on Earth's Magnetism
The understanding of Earth's magnetic field has evolved over centuries.
Early navigators relied on compasses, which pointed toward magnetic north, but the underlying reasons for this phenomenon were not well understood until the 19th century. Pioneering scientists like William Gilbert proposed theories regarding magnetism, laying the groundwork for future research. It wasn’t until the advent of geophysics in the 20th century that the dynamo theory gained prominence, providing a comprehensive explanation for the magnetic field's origin.
The Role of Solar Wind and Magnetic Field Interaction
The magnetic field not only protects the Earth but also interacts with solar wind, a stream of charged particles emitted by the sun. This interaction forms the magnetosphere, a region around the Earth that deflects most of these particles, shielding the planet from harmful radiation. Without this protective magnetic field, life as we know it would be significantly jeopardized, making the study of its origins and maintenance even more critical.
Variability and Reversals of the Magnetic Field
One fascinating aspect of the Earth’s magnetic field is its variability, including periodic reversals where magnetic north and south switch places. These geomagnetic reversals occur over thousands to millions of years and are recorded in the geological record. The last reversal, known as the Brunhes-Matuyama transition, occurred approximately 780,000 years ago.
Understanding these reversals helps scientists learn about the dynamics of the Earth’s core and the processes that govern its magnetic behavior.
Technological Implications of Earth's Magnetic Field
The Earth’s magnetic field has significant implications for technology. Satellites and other space vehicles must be designed to withstand the effects of the magnetic environment, as fluctuations can impact communication and navigation systems.
Additionally, understanding the magnetic field is crucial for predicting space weather events, which can affect power grids and satellite operations on Earth.
Future Research and Exploration
As our understanding of the Earth’s magnetic field continues to evolve, researchers are employing advanced technologies, such as satellite missions and computer simulations, to study the core's dynamics more closely. These studies aim to reveal not only how the magnetic field is generated but also how it may change in the future.
Insights gained from this research could have profound implications for our understanding of planetary formation and behavior.
Conclusion: The Significance of Earth's Magnetic Field
In conclusion, the Earth's magnetic field is a product of the dynamic processes occurring within its core. Understanding its origins and mechanisms is vital for appreciating its role in protecting life and facilitating technological advancements.
As we continue to explore and study this fascinating aspect of our planet, we deepen our understanding of the Earth and its place in the solar system.